How many Hollywood actresses does it take to write something like this?
Answer: One, if you are Natalie Portman.
By the way, Jonathan Safran Foer is one of my favourite young writers too.
--------
Jonathan Safran Foer's Eating Animals Turned Me Vegan
Jonathan Safran Foer's book Eating Animals changed me from a twenty-year vegetarian to a vegan activist. I've always been shy about being critical of others' choices because I hate when people do that to me. I'm often interrogated about being vegetarian (e.g., "What if you find out that carrots feel pain, too? Then what'll you eat?").
I've also been afraid to feel as if I know better than someone else -- a historically dangerous stance (I'm often reminded that "Hitler was a vegetarian, too, you know"). But this book reminded me that some things are just wrong. Perhaps others disagree with me that animals have personalities, but the highly documented torture of animals is unacceptable, and the human cost Foer describes in his book, of which I was previously unaware, is universally compelling.
The human cost of factory farming -- both the compromised welfare of slaughterhouse workers and, even more, the environmental effects of the mass production of animals -- is staggering. Foer details the copious amounts of pig shit sprayed into the air that result in great spikes in human respiratory ailments, the development of new bacterial strains due to overuse of antibiotics on farmed animals, and the origins of the swine flu epidemic, whose story has gripped the nation, in factory farms.
I read the chapter on animal shit aloud to two friends -- one is from Iowa and has asthma and the other is a North Carolinian who couldn't eat fish from her local river because animal waste had been dumped in it as described in the book. They had never truly thought about the connection between their environmental conditions and their food. The story of the mass farming of animals had more impact on them when they realized it had ruined their own backyards.
But what Foer most bravely details is how eating animal pollutes not only our backyards, but also our beliefs. He reminds us that our food is symbolic of what we believe in, and that eating is how we demonstrate to ourselves and to others our beliefs: Catholics take communion -- in which food and drink represent body and blood. Jews use salty water on Passover to remind them of the slaves' bitter tears. And on Thanksgiving, Americans use succotash and slaughter to tell our own creation myth -- how the Pilgrims learned from Native Americans to harvest this land and make it their own.
And as we use food to impart our beliefs to our children, the point from which Foer lifts off, what stories do we want to tell our children through their food?
I remember in college, a professor asked our class to consider what our grandchildren would look back on as being backward behavior or thinking in our generation, the way we are shocked by the kind of misogyny, racism, and sexism we know was commonplace in our grandparents' world. He urged us to use this principle to examine the behaviors in our lives and our societies that we should be a part of changing. Factory farming of animals will be one of the things we look back on as a relic of a less-evolved age.
I say that Foer's ethical charge against animal eating is brave because not only is it unpopular, it has also been characterized as unmanly, inconsiderate, and juvenile. But he reminds us that being a man, and a human, takes more thought than just "This is tasty, and that's why I do it." He posits that consideration, as promoted by Michael Pollan in The Omnivore's Dilemma, which has more to do with being polite to your tablemates than sticking to your own ideals, would be absurd if applied to any other belief (e.g., I don't believe in rape, but if it's what it takes to please my dinner hosts, then so be it).
But Foer makes his most impactful gesture as a peacemaker, when he unites the two sides of the animal eating debate in their reasoning. Both sides argue: We are not them. Those who refrain from eating animals argue: We don't have to go through what they go through -- we are not them. We are capable of making distinctions between what to eat and what not to eat (Americans eat cow but not dog, Hindus eat chicken but not cow, etc.). We are capable of considering others' minds and others' pain. We are not them. Whereas those who justify eating animals say the same thing: We are not them. They do not merit the same value of being as us. They are not us.
And so Foer shows us, through Eating Animals, that we are all thinking along the same lines: We are not them. But, he urges, how will we define who we are?

 I love children's drawing. They always make my day :). This one is from my friend M-Y's lovely kids, Evelyn and Oliver.
I love children's drawing. They always make my day :). This one is from my friend M-Y's lovely kids, Evelyn and Oliver. Watching
Watching  This is based on a
This is based on a  My Valentine's Day present - chocolate coated almonds from La Maison
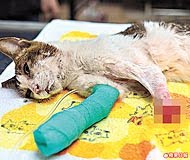
My Valentine's Day present - chocolate coated almonds from La Maison  When Pepper first joined our family, she was all-out neurotic. I couldn't blame her - shortly after we adopted her, we whisked her to the vet for double surgery. Now, after 15 months, she is totally at ease. One of my daily pleasures is waking up in the morning to find her sleeping by my thigh.
When Pepper first joined our family, she was all-out neurotic. I couldn't blame her - shortly after we adopted her, we whisked her to the vet for double surgery. Now, after 15 months, she is totally at ease. One of my daily pleasures is waking up in the morning to find her sleeping by my thigh. 










